Timing is crucial when it comes to taking a pregnancy test. The anticipation and anxiety that often accompany this period can be overwhelming, and many women want to know as soon as possible if they are pregnant. Fortunately, modern pregnancy tests offer early detection, making it easier to find out. But how early is too early, and what factors determine the right time to test?
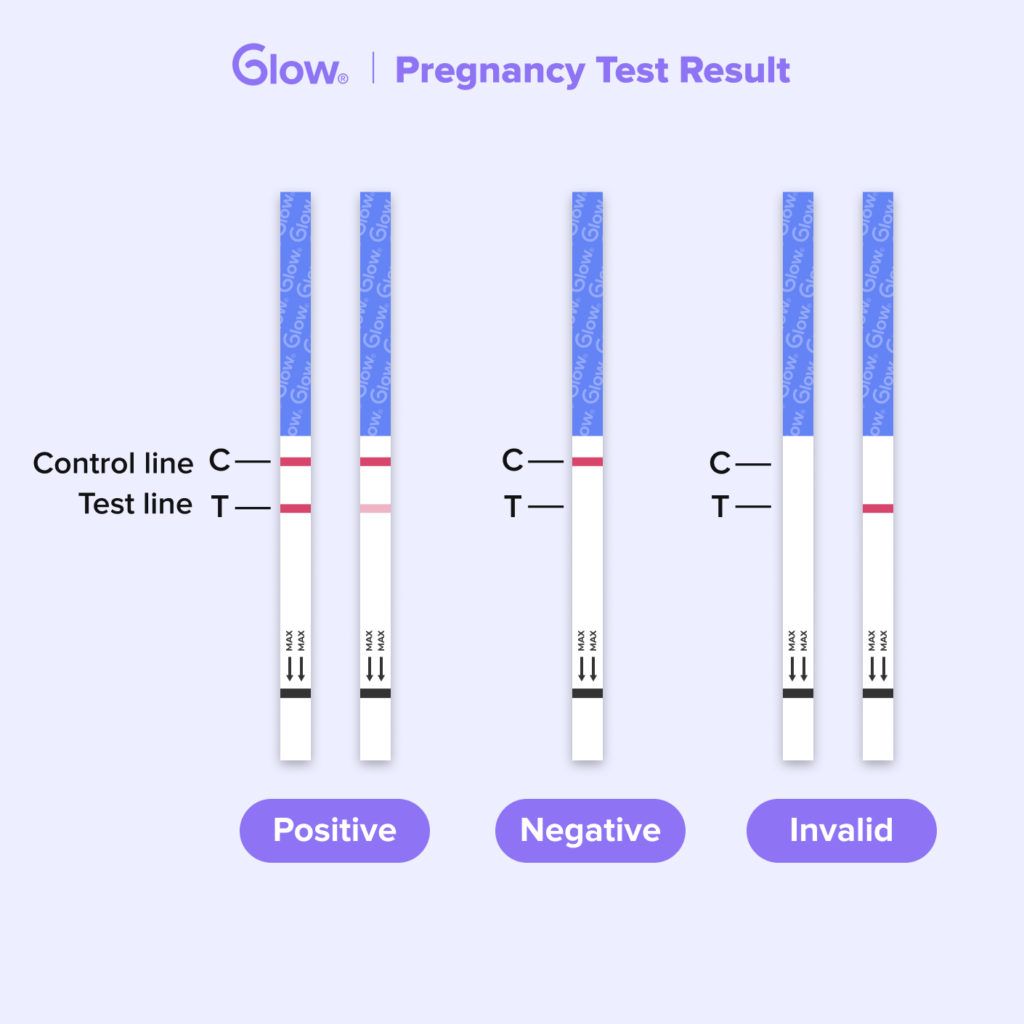
Pregnancy tests detect the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone produced by the placenta shortly after a fertilized egg attaches to the uterine lining. hCG can be detected in both blood and urine, but most over-the-counter home pregnancy tests rely on urine samples.
Types of pregnancy tests:
- Urine Tests: These are the most common home pregnancy tests that can be easily purchased over-the-counter.
- Blood Tests: Performed by healthcare providers, these tests can measure the exact amount of hCG in the blood and detect pregnancy earlier than urine tests.
Earliest Time to Take a Pregnancy Test
The timing of taking a pregnancy test can significantly impact its accuracy. Here’s what you need to know:
1. Conception and Implementation: After conception, the fertilized egg travels down the fallopian tube and implants itself into the uterine wall. This implantation typically occurs about 6-12 days after ovulation.
2. hCG Production: Once implantation occurs, hCG begins to be produced and enters the bloodstream first, and then appears in the urine. The levels of hCG double approximately every 48 to 72 hours.
3. Earliest Time for Testing:
Urine Tests: Home pregnancy tests vary in sensitivity. Generally, it’s recommended to take a test after a missed period. However, some early detection tests claim they can be used a few days before the missed period, often up to 6 days earlier.
Blood Tests: Because they measure the exact amount of hCG, blood tests are more sensitive than urine tests. They can detect pregnancy approximately 7-12 days after ovulation—often before a missed period.
Factors Affecting Test Timing
Ovulation and Menstrual Cycle Variability
The timing of ovulation can vary significantly, even in women with regular cycles, which impacts when to test. Women with irregular cycles may find it even more challenging to determine the optimal testing day. For more information, see When Does Ovulation Occur? Understanding the Timing, Process, and Signs.
Sensitivity of Test Brands
Different pregnancy tests have different sensitivity levels, measured in milli-international units per milliliter (mIU/mL). Tests with higher sensitivity can detect lower levels of hCG (e.g., 10 mIU/mL) and thus can be used earlier.
Individual hCG Production
The rate at which hCG levels rise can differ from woman to woman. Some might produce hCG rapidly, detectable within days of implantation, while others might take longer.
Accuracy of Early Pregnancy Testing
Many home pregnancy tests claim to be over 99% accurate when used from the first day of the missed period. However, real-world accuracy may be lower due to factors like improper usage.
- Testing Too Early: This increases the risk of a false negative result, where the test indicates you are not pregnant even though you are, because hCG levels may not be high enough for detection.
- Diluted Urine: Drinking a lot of water before the test can also lead to false negatives.
- Medical conditions: Less common but possible, false positives can occur due to certain medications, medical conditions, or residual hCG following a recent pregnancy or miscarriage.
For best accuracy, follow the test guidelines closely, ideally test after a missed period, and use the first morning urine, when hCG concentration is the highest.
Symptoms Indicating When to Test
Common early pregnancy symptoms include missed periods, breast tenderness, nausea, and fatigue. However, these symptoms can also be due to other factors and are not conclusive.
What to Do After Testing
Negative Results: If you receive a negative result but still don’t get your period, wait a few days to a week and test again. Hormone levels may not have been high enough to detect initially.
Positive Results: A positive result should be confirmed with a healthcare provider, who can provide further guidance and care.
Repeat Testing: Retesting might be necessary if initial results are unclear or if symptoms persist without a positive test.
Taking control of your reproductive health means being informed and proactive. Knowing when and how to take a pregnancy test can reduce anxiety and ensure you get the most accurate results. Remember, we’re here to empower you with information every step of the way.