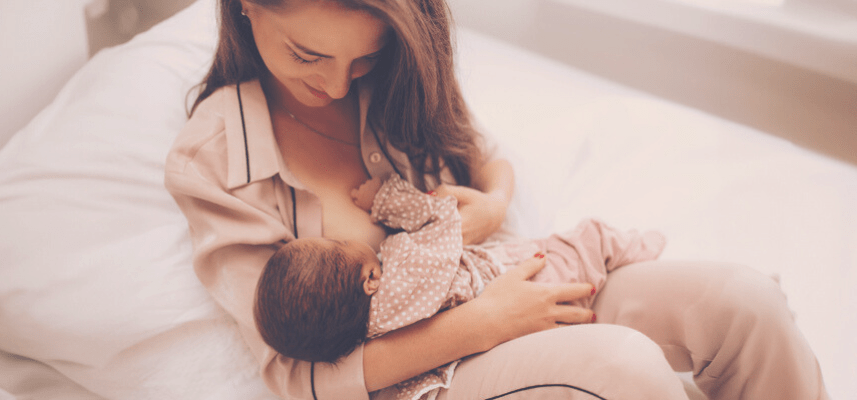
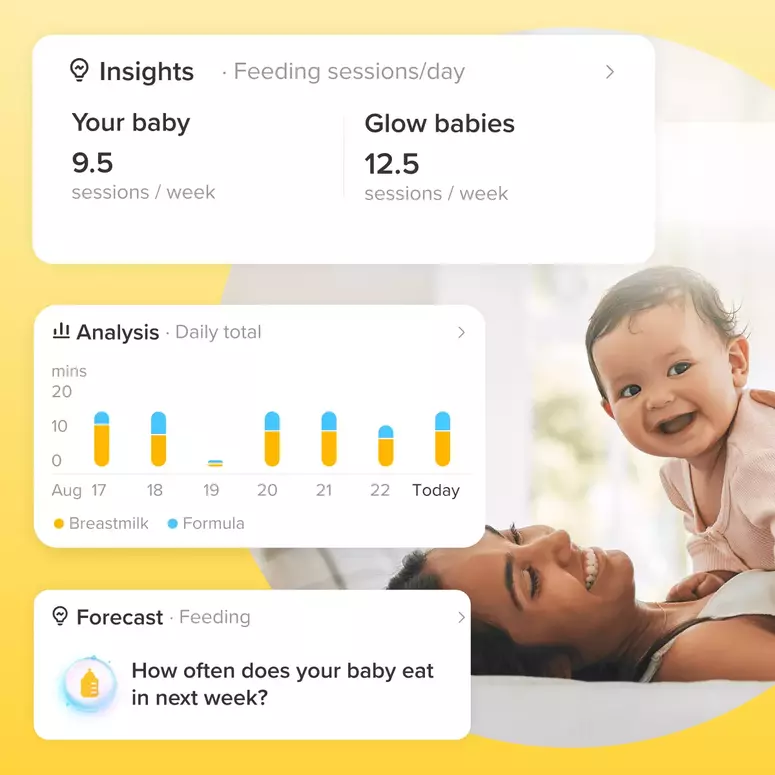
Breastfeeding provides unparalleled nourishment for infants, yielding a multitude of benefits for both mother and child. This natural process not only fosters a strong emotional bond but also delivers a perfect balance of essential nutrients and vital protective antibodies. Leading health organizations, including the WHO and AAP, advocate for exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months, followed by continued breastfeeding with complementary foods for up to two years or beyond.
Benefits for the Baby:
Breast milk provides optimal nutrition, dynamically adapting its composition of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals to meet a baby’s evolving needs. Crucially, it bolsters the infant’s immune system with a rich supply of antibodies, offering protection against infections and illnesses like ear infections, respiratory infections, and diarrhea. Research further indicates that breastfeeding reduces the risk of chronic diseases, including asthma, allergies, type 1 diabetes, and obesity, later in life. It also supports healthy growth and optimal brain development, and studies have shown a reduced risk of Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS).
Benefits for the Mother:
Breastfeeding offers numerous benefits for mothers, contributing to physical recovery by aiding uterine contraction and reducing postpartum bleeding, while also lowering the long-term risk of chronic diseases such as breast and ovarian cancer, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. The intimate physical contact during breastfeeding fosters a strong emotional bond between mother and child. Additionally, breast milk’s immediate availability and optimal temperature provide unparalleled convenience, especially when traveling. Furthermore, breastfeeding can assist mothers in returning to their pre-pregnancy weight.