Tracking Ovulation with Irregular Periods: The Best Tools to Use
Even with regular cycles, figuring out when you’re ovulating can be tricky. You may have heard that ovulation typically occurs mid-cycle, but what about when "mid-cycle" is a moving target?
You might find that some of the more traditional ovulation-tracking methods don’t work for you when you have irregular periods. Don’t worry—all is not lost. We’ll walk you through the best ways to track your ovulation when your periods don’t come as regularly as you’d like.
What exactly are irregular periods?
A “typical” menstrual cycle lasts 28 days (measured from the start of one period to the next). Your periods are considered irregular if any of the following is true: 1
- Your menstrual cycle is consistently shorter than 21 days or longer than 35 days
- The length varies by more than 9 days from one month to the next
- You miss three or more periods in a row
Many women have irregular cycles, and having one isn’t necessarily anything to worry about (although sometimes, it can also be caused by underlying health conditions, which we’ll expand on below).
Even if your irregular cycle doesn’t indicate a problem, it can make predicting when you’ll ovulate (i.e., when you’ll enter your fertile time each month) very hard. This, in turn, can make it hard to get pregnant.
Why tracking ovulation with irregular periods is so difficult
Tracking ovulation when your periods are irregular is tricky because many of the methods work under the assumption that, like many women, you have a 28-day cycle.
If you did, you’d usually ovulate around day 14, meaning you could just count forward from the first day of your cycle (when you got your last period). 2 This is known as the calendar method, and it’s the one used by most online ovulation calculators.
If you have irregular periods, you may not ovulate around the same time each month, which makes this method hard or impossible to pull off. The degree of difficulty depends on what type of irregular cycle you have:
- Regularly irregular: Some women have “irregular” cycles that are shorter or longer than average but still consistent (e.g., around 40 days instead of 28). If that’s you, you can still use the calendar method, just with small adjustments (like counting forward by 20 days instead of 14). 3
- Irregularly irregular: If you have truly erratic cycle lengths (e.g., a 28-day cycle, followed by a 35-day cycle, then a 40-day cycle), the calendar method won’t be viable at all. You’ll need a more sophisticated method to predict your ovulation.
If you have no clue which type you are, consider using a period tracker for a few months to find your cycle length and regularity.
How each stage of your cycle affects when you get your period
Your menstrual cycle is a more complex process than you might think. It has four distinct phases, and if just one of those is delayed or interrupted, it can have a cascading effect on the rest of your cycle, causing irregular periods.
The four phases of your menstrual cycle are: 4
- Menstruation: Your cycle starts when you get your period, and your body sheds the uterine lining built up from your previous cycle.
- Follicular phase: After your period, your estrogen levels rise, which thickens the uterine lining. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) encourages your ovarian follicles to develop, with one maturing into an egg. (Notably, as you get older and closer to menopause, your body begins producing more FSH, which can make your periods shorter or otherwise irregular.) 5
- Ovulation: After the follicular phase, your levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) surge, which causes one of your follicles to release a mature egg. The egg survives for just 12–24 hours, so if you’re struggling to determine when ovulation occurred, it’s easy to miss this narrow window. 2
- Luteal phase: The released egg travels down the fallopian tube, and your body produces progesterone, which thickens your uterine lining so the egg can implant in it. But like the menstrual and follicular phases of your cycle, the luteal phase may last longer than normal (10–17 days) if your periods are irregular. 6
If your egg is fertilized and successfully implants, then you’re pregnant. Otherwise, the uterine lining sheds, and you get your period.
Bleeding doesn’t necessarily mean that you ovulated
Not all bleeding is a sign that you ovulated or got your period. It’s possible to have vaginal bleeding in an anovulatory cycle (a menstrual cycle without ovulation), known as abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB). 7
How to track and predict ovulation with irregular cycles
Again, if you have genuinely unpredictable periods, the calendar method won’t work for you, but you can still track when you ovulate (and maybe predict when you’ll ovulate next month) with more sophisticated tools and methods.
Some of these methods help you tell if you’re ovulating (or are due to ovulate) now. Others are “looking forward” methods; if you use them consistently for several months, you’ll come to know your body better and may get an idea of roughly when you’ll ovulate after each period.
Ovulation tests
Ovulation tests, also known as ovulation predictor kits (OPKs), work by detecting a surge of LH in your urine, which usually happens between 16 and 48 hours before ovulation. 8 Your chances of getting pregnant when you see a positive ovulation test result are usually quite high if you have sex soon after.
By and large, ovulation tests are accurate and far more useful to women with irregular periods than the calendar method. When used correctly, they’re 90% accurate—unless your irregular periods are caused by polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). 9 10
PCOS makes it tricky to track your ovulation because it can cause mildly elevated levels of LH throughout your cycle. This, in turn, can cause OPKs to return false positives. 11 Getting pregnant with PCOS can be tricky, so speak to your doctor or a fertility specialist.
How to use an ovulation test
To use an ovulation test, you either place the test strip in your urine stream or collect a sample of your urine and dip the strip in it.
Ovulation test strips generally have two lines: a control line and a test line. If you get a positive result on your ovulation test (i.e., your levels of LH are surging), the test line will be as dark or darker than the control line. With a negative result, the test line will be faint or not visible at all.
If you have irregular cycles, it’s best to test frequently. Ideally, you’ll start testing right after your period ends and continue daily until you identify an LH surge or your next period begins.
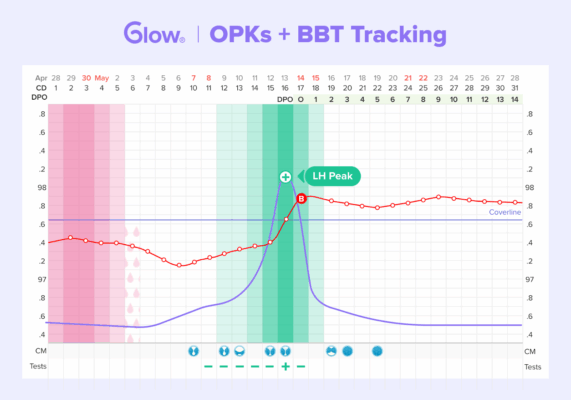
Basal body temperature charting
Your basal body temperature (BBT) is your body’s lowest resting temperature, which you usually reach first thing in the morning.
Proponents of BBT tracking claim that your resting temperature rises slightly during ovulation. It’s normally around 96º F–98º F for most people, but during ovulation, it may rise to 97º F–99º F. 12
The idea is that by regularly charting your BBT (at the same time each day through multiple cycles), you’ll notice patterns that will tell you when you’re ovulating. Even if your periods are irregular, you can allegedly still spot a shift.
Before you purchase a basal thermometer, know that various studies have shown that the way your cycle affects your BBT is unpredictable, so it’s not a surefire method for determining your fertile window. 13 14 15
You can try BBT charting, if you like—but don’t rely on it. It’s best used in conjunction with other methods.
Tracking ovulation symptoms
Often, you can look to your own body for clues about your fertility. Many women experience ovulation symptoms, so even if you have irregular periods, your body could still tell you when you’re most fertile.
For instance, many women notice that the consistency of their cervical mucus changes when they ovulate, often growing thicker and taking on the appearance of raw egg whites (many women even refer to it as egg white discharge). 16
Along with this ovulation discharge, you can also look out for other symptoms of ovulation: 16
Not all women have symptoms when they ovulate, so this method won’t work for everyone, but it’s worth a try. You can keep track of your symptoms (and your BBT) in a notebook or use a fertility tracker app.
Note that the intensity of your ovulation symptoms doesn’t correspond to your odds of conceiving. As an example, there’s no link between ovulation pain and pregnancy success. The presence of symptoms is just another potential clue that you’re approaching your fertile window for that month.
When to speak to your doctor about your irregular periods and fertility
Even if you’re diligently tracking with various methods, you might still struggle to figure out when you’re ovulating.
If you’re trying to get pregnant with irregular periods, consider speaking to your doctor or a fertility specialist, especially if you’ve been trying to get pregnant for over a year (or six months if you’re over 35) with no success.
Your doctor can give you more personalized fertility guidance and will check if your irregular cycles are being caused by an underlying medical issue.
Which medical issues can cause irregular periods?
As mentioned, the medical conditions that can cause irregular periods include:
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): This can make your ovaries produce an excess of hormones called androgens, which throw your reproductive hormones out of balance, resulting in irregular menstrual cycles. 9
- Endometriosis: This condition causes tissue that’s similar to the lining of your uterus to grow elsewhere in your body, often in your fallopian tubes or ovaries. It can lead to heavy bleeding before, during, and after your periods. 17
You may also get irregular periods if you suffer from thyroid conditions or are using medications like steroids or anticoagulants (blood thinners). 1
What else can cause irregular periods?
Along with medical conditions, your lifestyle can also cause irregular periods. They can be the result of: 1
It’s possible that simple lifestyle changes will be enough to get your periods back on track. Chat with your doctor about how to do this (or if you’re struggling to do so).
Are there medical treatments for irregular periods?
Yes, there are options for treating irregular cycles that you can discuss with your doctor. They may be able to prescribe drugs that regulate or even induce ovulation. You might also want to look into assisted reproductive technologies (ARTs), like in vitro fertilization (IVF), if you’re having trouble conceiving naturally.
Can you still get pregnant naturally if you have irregular periods?
Yes—you don’t necessarily need medical intervention to get pregnant with irregular periods. If you’re ovulating, even irregularly, there’s still a chance of conception.
If you manage to successfully spot patterns in your cycle (e.g., changes to your cervical mucus), the next step is to plan sex accordingly.
Your best chances of conception are in the 5 days leading up to ovulation, the day you ovulate, and the day after. That’s because sperm can survive in your reproductive tract for up to 5 days. If you time sex around that period, there’s a good chance you’ll get pregnant.
If you can’t get a handle on your cycle even with the methods listed above, your best bet is to just have sex frequently instead of trying to time it around ovulation. (Don’t stress yourself out by trying to do it every day—as long as you’re trying regularly, you probably have a decent shot.)
Other tips for boosting fertility
Keep your body in tiptop condition by: 19
- Eating a balanced diet
- Limiting stress
- Getting enough rest
- Cutting back on excessive exercise
- Maintaining a healthy weight
Often, these simple lifestyle changes may get your periods into a more predictable rhythm and increase your chances of getting pregnant.
Final thoughts
It’s no easy task trying to figure out your fertile period when you have to contend with irregular periods.
However, there are still ways to track and predict ovulation. It might take a little longer for you to notice the unique patterns in your cycle, but it’s doable. Keep up the hard work, talk to your doctor if you’re really struggling, and remember, it only takes one healthy egg and some well-timed sex to get that bun in the oven!
Article Sources
- Cleveland Clinic. "Irregular Periods" Retrieved May 27, 2025.
- Cleveland Clinic. "Ovulation" Retrieved May 27, 2025.
- UCLA Health. "What you need to know about irregular periods" Retrieved May 27, 2025.
- Cleveland Clinic. "Menstrual Cycle" Retrieved May 27, 2025.
- Association of Reproductive Reflexologists. "What is the follicular phase (and why do you need to know about it when trying for a baby?)" Retrieved May 27, 2025.
- Cleveland Clinic. "Luteal Phase" Retrieved May 27, 2025.
- Cleveland Clinic. "Anovulation" Retrieved May 27, 2025.
- ColumbiaDoctors. "Find Your Ovulation Day" Retrieved May 27, 2025.
- Cleveland Clinic. "Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)" Retrieved May 27, 2025.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. "Ovulation (Urine Test)" Retrieved May 27, 2025.
- You and Your Hormones. "Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)" Retrieved May 27, 2025.
- Planned Parenthood. "What’s the temperature method of FAMs?" Retrieved May 27, 2025.
- Fertility and Sterility. "Accuracy of Basal Body Temperature for Ovulation Detection" Retrieved May 27, 2025.
- Fertility and Sterility. "Basal body temperature: unreliable method of ovulation detection" Retrieved May 27, 2025.
- Fertility and Sterility. "Inaccuracy of basal body temperature charts in predicting urinary luteinizing hormone surges" Retrieved May 27, 2025.
- American Pregnancy Association. "Ovulation Symptoms – Am I Ovulating?" Retrieved May 27, 2025.
- Johns Hopkins Medicine. "Endometriosis" Retrieved May 27, 2025.
- Nemours TeensHealth. "Irregular Periods" Retrieved May 27, 2025.
- Mayo Clinic. "Getting pregnant" Retrieved May 27, 2025.




